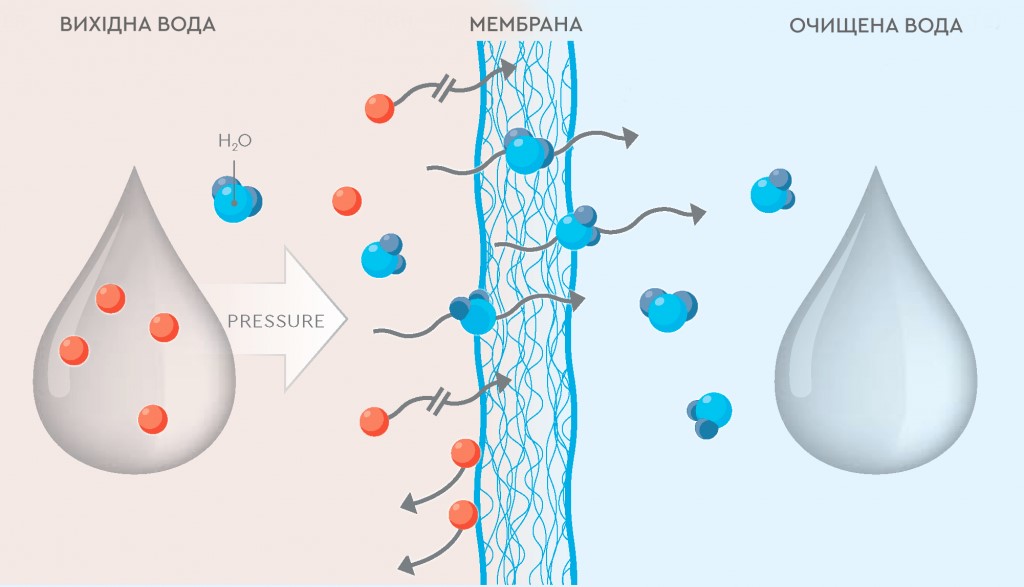
Thanks to the properties of reverse osmosis membranes and the physics of the process itself, reverse osmosis allows you to remove the smallest particles of pollution, including viruses and even metal ions.
After purifying the water, we get distillation (this is how it is produced in modern industrial processes).
-
Comparison of filtration technologies
If you compare reverse osmosis with other membrane processes, it can be argued that it is the most effective water purification technology.
Why so?
The figure shows a comparison of reverse osmosis with other filtration methods.
To begin, we will consider other methods of phase separation or filtering.
Conventional filtration – includes the removal of large particles of pollution (provided that they can be felt and seen with the naked eye) – sand, rust, mud.
The size of these particles is from 1000 µm (1 mm) to 1 µm.
Processes for separating such particles from the liquid phase are developed in bulk, cartridge, disc, bag, wash and other types of filters. Such processes are usually used during pre-treatment of water.
The advantage of simple mechanical filtration is that it can occur at low pressure, for example, filtration in filling filters is most often done without pressure injection, and cartridge filters in everyday life work with the pressure created by the pipeline.
Microfiltration is the process of removing particles of 1 to 0.1 µm in size from water. They include bacteria, large paint molecules, pesticides, gelatin, emulsion latex.
Microfiltration processes are not widely used in drinking water preparation technology, but are widely used for the treatment of wastewater and technical water for industrial processes.
Ultrafiltration allows you to remove small particles from 0.005 to 0.1 microns in size (viruses, particles of some proteins, particles of medical drugs, etc.). The processes are widely used for the preparation of drinking water in European countries. Ultrafiltration can be considered the best method for preparing clean drinking water. Also, these processes are widely used in the pharmaceutical and food industries.
The use of ultrafiltration in everyday life is limited due to the fact that this process does not remove impurities of ionic size (hardness salts, heavy metals, nitrates) and they pose a significant risk to humans.
Reverse osmosis is capable of removing particles as small as 0.001 microns, which ensures the removal of contaminants of ionic size (hardness ions, heavy metals, nitrates, sulfates, etc.).
Reverse osmosis technologies are often used in the preparation of drinking water, in the distillation preparation processes for steam boilers, in the food industry.
Now we will consider the types of reverse osmosis installations and their application, starting from household appliances and ending with large industrial processes.
-
What is a membrane?
There are three types of reverse osmosis membranes: roll, semi-fiber and flat.
The “roll” membrane consists of a housing and, in fact, a filter element
Inside the roller there is a perforated tube, which serves to create the strength of the element, to collect the purified water and as a basis for wrapping the membrane in the production process. A thick layer of semi-permeable polyamide membrane fabric is wrapped over it.
During the filtration process, water enters the thickness of the fabric and collects in the tube.
Thanks to this design, these membranes have the highest performance, minimal material consumption and take up less space. Therefore, roll membranes are the most common in the world and occupy 95% of the industrial market.
5% are devices with flat membrane elements and devices for preparing water based on hollow fibers.
-
Production of reverse osmosis membranes
The world leader in the production of membrane elements is the FilmTec Corporation – a structural unit of the DOW Chemical Corporation (USA). The production of the membrane elements is carried out directly in the USA.
The company’s membranes are certified worldwide for water treatment for both drinking and industrial purposes.
DOW FilmTec membranes with a diameter of 2.5 “- 4″ – 8” are presented in several series for the main types of water:
-
XLE – for fresh;
-
BW – to salt;
-
SW – for the sea and water with a high level of salinity.
The official importer of “DOW FilmTec” membranes in Ukraine since 1995 is the “Ekosoft” company.
And since 2017, the company has started producing its membrane elements from American canvas, which made it possible to make reverse osmosis technology cheaper.
Reverse osmosis membrane feed water requirements
The membrane fabric is made of a very sensitive material, therefore the quality of the water entering the cleaning must strictly correspond to the allowed values:
-
not more than 0.56 mg/l suspended substances;
-
oxidizability – less than 4 mgO 2 / l;
-
free chlorine less than 0.1 mg/l;
-
temperature of supplied water – 4 – 30 °C;
-
iron – up to 0.1 mg/l;
-
manganese – up to 0.05 mg/l;
-
hardness – up to 3 mg-eq/l.
Some of the parameters (iron, manganese, silicates) may be higher than the declared rates in the case of the use of antiscalants (special substances that prevent the deposition of sediment on the surface of the membrane).
Other parameters are achieved through pre-treatment, which may include mechanical filtration, softening, iron removal or adsorption, depending on the initial water parameters.
Reverse osmosis systems
HOME FILTERS WITH REVERSE OSMOSIS
Domestic reverse osmosis filters are a complex technology of fine water purification from impurities of various natures. The filtration process looks like this: water from the tap enters the pre-cleaning unit, which includes the following stages:
PRIOR CLEANING
-
removal of mechanical impurities larger than 5 μm – sand, rust, scales, algae particles, etc.
The process takes place in a foamed polypropylene cartridge. Such cartridges are made of high quality food grade polypropylene.
-
adsorption of organic impurities and chlorine;
Adsorption is the absorption of certain substances from the inner surface of solid bodies due to intermolecular interaction forces. Adsorption processes take place in special materials – sorbents (activated carbon, xerogels, aluminum, etc.). The most common sorbent in water treatment technologies is activated carbon obtained from natural raw materials (coconut and walnut shells, wood).
The substances that are removed from the water in the process of such cleaning are called adsorbate, they contain organic impurities and organic chlorine, pesticides and active chlorine.
The suction filter cartridges are a polymer body filled with high quality activated carbon obtained from coconut shells.
-
final cleaning.
There are two options for final cleaning: a cheap one using a cartridge made of foamed polypropylene with a filtration rate of 1 μm and an expensive one using a cartridge in the form of a compressed carbon block, which, in addition to mechanical dirt , also removes organic and chlorine residues.
The importance of this phase is the protection of the membrane element from blocking with particles of large pollution and chlorine, which can cause its damage and failure.
MEMBRANE CLEANING
99.8% of impurities are removed from the water, including viruses, bacteria and heavy metal ions.
The membrane is a housing membrane holder containing a tightly wound polymer membrane element.
The membrane element consists of semipermeable polymer fibers. The housing of the membrane holder is made of high quality food grade plastic.
Inside the membrane module, the water is divided into two streams – concentrate and permeate. The concentrate is poured into the sewer, and the permeate is used for deodorization and mineralization (if provided).
DEODORIZATION OF WATER BY PASSING IT THROUGH A POSTFILTER MADE OF ACTIVATED CARBON
Thanks to the unique properties of coconut charcoal, water passes through it, has a pleasant sweet taste and is absolutely safe for humans.
THE MINERALIZATION PHASE
In this stage, the water passes through a filter filled with natural rocks that are capable of limited solubility in water. As a result, the user receives water saturated with useful minerals in the necessary amount, which improves the taste of water and makes it as useful as possible for the human body.
Mineralization is not a mandatory stage of water purification and can be installed optionally.
Maintenance of domestic reverse osmosis filters for drinking water includes replacement of cartridges (usually once every 3 months), membrane and filter (once a year) and mineralizer (once every 6 months).
To understand in more detail the details of the operation of a home reverse osmosis filter, we recommend watching the video.
COMMERCIAL REVERSE OSMOSIS SYSTEMS
These systems are intended for the preparation of purified water for large private houses, hotels, restaurants, water factories, bakeries, breweries, steam boilers, greenhouses, laboratories.
A commercial reverse osmosis system is fundamentally different from a home one. First, it provides a much larger volume of purified water and secondly, it requires a higher applied pressure to maintain this performance. Commercial water treatment includes systems that provide a water volume of up to 30 m 3 / days, the systems with the highest productivity already belong to the industrial ones.
The water enters the prefilter, where it is cleaned of mechanical impurities larger than 5 microns (this is necessary to avoid damage and failure of the expensive membrane element).
After preliminary cleaning, it enters the membrane module, where it is separated into two streams: purified water (permeate) or dirty water (concentrate). A part of the concentrate goes to the sewer, and a part goes to the high pressure pump to ensure the recycling of the concentrate.
Also, before supplying water to the membrane, depending on its quality, an antiscalant can be used, which prevents the formation of deposits on the membrane.
Control of such installations is carried out using a controller that performs a number of functions:
-
turning the installation on and off when filling and emptying the storage tank;
-
signaling and disconnection of the installation in emergency situations;
-
continuous control of the quality of purified water (total salinity and temperature).
Despite the presence of a cartridge filter for water pre-purification, in case of heavy contamination, it is recommended to install more advanced filtration systems, for example, adsorption filters for chlorine removal for highly chlorinated and organically contaminated water. Always keep in mind that the filter material of the membrane element is “afraid” of chlorine.
Reverse osmosis system maintenance includes chemical washing to remove deposits on the membrane and replacement of pre-cleaning cartridges.
We also recommend that you watch a video about commercial reverse osmosis systems.
INDUSTRIAL REVERSE OSMOSIS SYSTEMS

Industrial reverse osmosis systems are large units designed for use in large enterprises in various industries:
-
chemical;
-
desalination of sea water;
-
thermal;
-
food;
-
Textile;
-
paper etc.
The productivity of industrial reverse osmosis systems reaches 50 m 3 / hour. Productivity is limited by the number of membrane elements and industry needs.
We hope we have answered your question about what is reverse osmosis. You may also be interested in other articles: